The “ECB effect”

The ECB unanimously raised interest rate by 75 basis points on Thursday, stressing on the fact that the unconditional policy priority is to suppress inflation. Growth forecasts proved to be somewhat unexpected - the regulator not only ruled out a recession next year, predicting growth of 0.9%, but also revised forecast for economic growth this year from 2.8% to 3.1%, citing positive surprises in the first half of the year.
Another hawkish signal was a change in long-term inflation forecasts. The ECB revised its inflation forecast for 2024 from 2.1% to 2.3%, signaling that the economy is likely to demand more rate hikes as inflation returns to its target more slowly than previously thought.
Below is a comparative table of the economic forecasts of the two past meetings of the ECB. The market expected more pessimistic numbers:
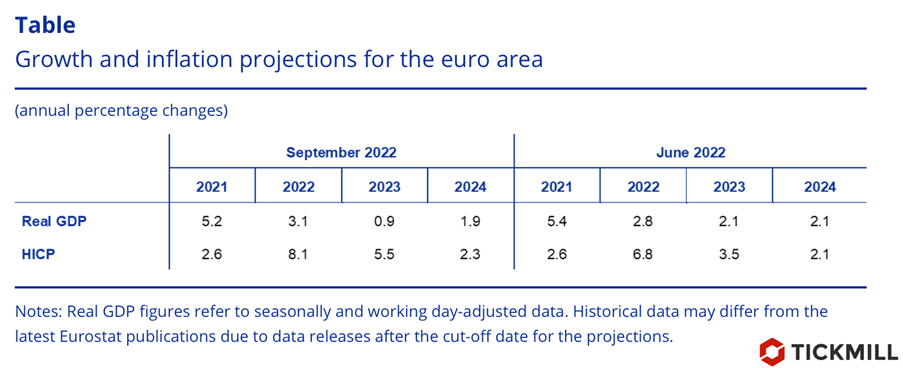
The ECB's optimistic estimates of economic growth andinflation diverged sharply from the market consensus, which has been factoringin a recession in asset prices due to the energy crisis. A tectonic shift inexpectations has triggered a massive sell-off in the fixed-income market, withGerman 10-year bonds offering nearly 1.8% today, about 20 basis points abovepre-ECB yields:

The outlook of the credible forecaster represented by the ECB, which somewhat downgraded the impact of the energy crisis on the economy, allowed investors to breathe a sigh of relief and resume the yield hunt. The dollar collapsed, European currencies rebounded, and the cyclical AUD and NZD gained more than 1.5% on expectations that the upswing phase would last longer than previously thought. The “stretched spring” on USDJPY bounced the most – the intraday drop was almost 2%.
Risk demand is likely to continue recovering next week as the US inflation report due on Tuesday is next in line. There is a strong temptation to bet on a downside surprise (inflation lower than market consensus) in market prices, as the volatile components that accelerated headline inflation earlier contributed negatively in August. U.S. new car sales declined m/m (-1.1%), suggesting that the monthly increase in car prices will be negligible, while gasoline prices fell from $1.2 to $1.05 per liter:
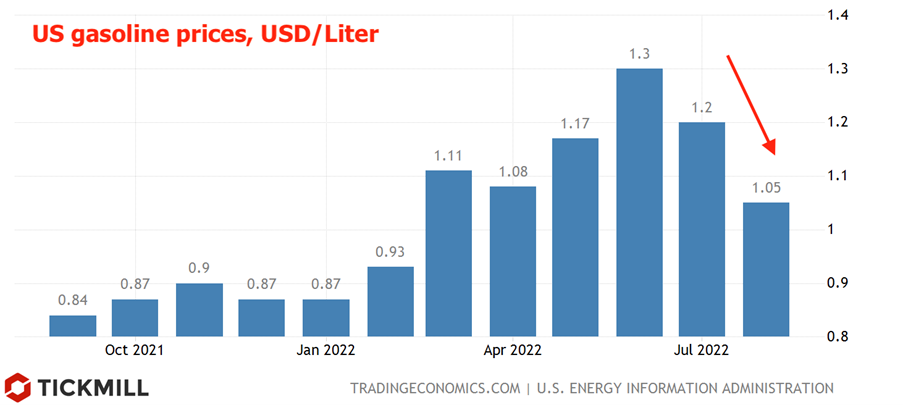
The faster inflation falls, the higher the chance that the Fed will try to correct market expectations on the pace of rate hikes. Despite Powell's unshakable position at Jackson Hole, it must be remembered that at the end of 2021 the Fed could not even imagine that in six months it would raise the rate by 2% within just three months.
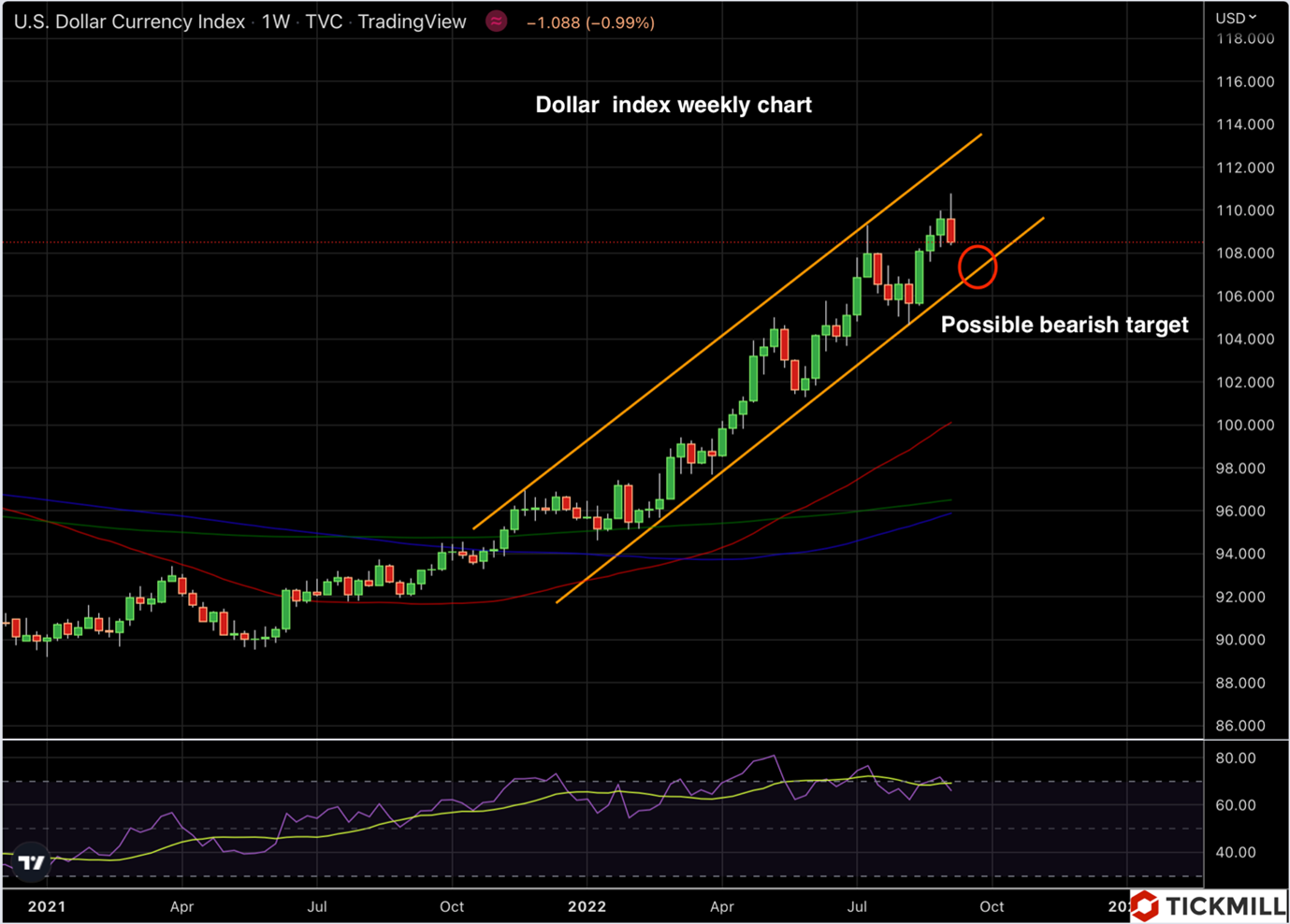
The dollar correction target is 107.50 on the index (DXY):
Disclaimer: The material provided is for information purposes only and should not be considered as investment advice. The views, information, or opinions expressed in the text belong solely to the author, and not to the author’s employer, organization, committee or other group or individual or company.
Past performance is not indicative of future results.
High Risk Warning: CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 72% and 73% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with Tickmill UK Ltd and Tickmill Europe Ltd respectively. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Futures and Options: Trading futures and options on margin carries a high degree of risk and may result in losses exceeding your initial investment. These products are not suitable for all investors. Ensure you fully understand the risks and take appropriate care to manage your risk.
